Introduction
Economic analysis is considered as evaluation that helps in understand the economic conditions. With an assistance of this, the number of policies and programs are being designed so that issues can be resolved. It mainly focuses on cost analysis, fiscal impact, cost effectiveness, etc (Ricard, 2016). Current report is focused towards economic conditions before price ceiling and after application of deregulation. It will provide understanding about market of tertiary education in both circumstances so that better policies can be designed to improve economic conditions. It will also present the impact of deregulation on efficiency and equity aspects.
The Market for Tertiary Education
As per the detailed study, it can be said that binding of price ceiling allow to have increase in surplus of supply and lead to decrease in economic surplus. It clearly indicates that market of tertiary education has also faced advancement in supply because it allows government to offer education services at low cost. By having effective development of price ceiling the economic impact can only be taken into account if economic aspects are less as compared to free market equilibrium price (Robert, 2015). In addition to this, it can be said that an effective price ceiling has lowered the price of education programs which has negatively impacted on the surplus of provider. It means the end price of tertiary education can also decrease which attracts citizens to prefer education after high school.
It has been noticed that supply of services was low because the demand of tertiary education programs was high due to low pricing of programs. It indicates that the price ceiling has also impacted positively on literacy rate because number of people has attracted to join programs. In this, ratio of undergraduate programs has also been increased (Nordhaus, 2010). The courses that takes up to four years were key preferences of people and students because low cost education is always a preference of citizens. It has also been witnessed that low pricing of diplomas and other certificate courses has increased the demand in great context which has negatively impacted on supply. If a ceiling is to be imposed for a long period of time, a government may need to ration the product to ensure availability for the greatest number of consumers (Perkins and Neumayer, 2015). It is one of key reason that federal government of experimentia has also focused on limiting the availability of seats in the courses so that supply can be managed in appropriate manner. It has also allowed government to make sure that availability of courses for citizens is maintained by focusing on ration of information. It has been witnessed that price ceiling increases the demand that causes supply shortage which might also create a better opportunity for black market. It means number of people has entered in market who has started providing seats in education institutes on the basis of donation (Roberts and Kingsbury, 2008). People that are not qualified but rich by nature may create black market for the programs. It might affect the effectiveness of education system in negative manner so government need to ensure on it.
In addition to this, it can be said that application of price ceiling in tertiary education has enhanced the level of government contribution in education system. It has increased the level price ceiling and decreased the economic strength of Federal Government of Australia. Government contribution is really high in context to dentistry that increases the demand and decreases the level of supply. It means government need to take initiatives so that supply and demand can be managed in appropriate manner.
Below graph, indicates that level of private sector organisation is not much high due to level of price ceiling. By having improved focus on free market and deregulation the issue might be overcome and lead business to impressive level of success. It also indicates that economic condition of Australia is less as compared to other nation because of price ceiling in regard to tertiary education.
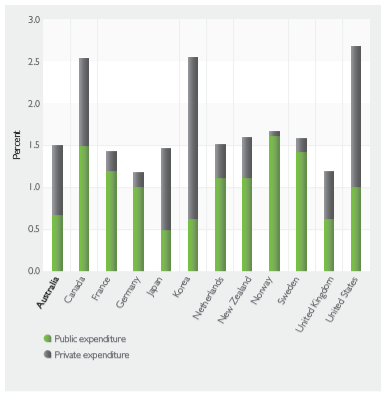
Illustration 2: Public and Private Expenditure
References
- Hook, R.C. and Czinkota, M.R., 2013. Export activities and prospects of Hawaiian firms. Asia Pacific International Journal of Marketing.
- Jetschke, A. and Murray, P., 2012. Diffusing regional integration: the EU and Southeast Asia. West European Politics.
- Morley, J.W., 2015. Driven by Growth: Political Change in the Asia-Pacific Region. Routledge.
- Nordhaus, W. D., 2010. Economic aspects of global warming in a post-Copenhagen environment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
- Perkins, R. and Neumayer, E., 2015. The international diffusion of new technologies: A multitechnology analysis of latecomer advantage and global economic integration. Annals of the Association of American Geographers.
- Ricard, B., 2016. Price ceiling impact. Sage.
- Robert, C., 2015. Deregulation and its impact on policies. Roughtledge.














